Preliminaries
1.1 Standard form LP
关键元素:
1.\(n\)个variables:\(x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_n\)
2.1个objective function:\(\mathbf{z} = c_1 x_1 + c_2 x_2 + \cdots + c_n x_n\)
3.\(m\)个constraints:
\[\begin{aligned} a_{11}x_1 + a_{12}x_2 + \cdots + a_{1n}x_n = & \ b_1 \\ a_{21}x_1 + a_{22}x_2 + \cdots + a_{2n}x_n = & \ b_2 \\ \vdots & \\ a_{m1}x_1 + a_{m2}x_2 + \cdots + a_{mn}x_n = & \ b_m \\ \end{aligned}\]4.非负:\(x_1 \ge 0, x_2 \ge 0, \ldots, x_n \ge 0,\)
Explicit form
Minimize \(\mathbf{z} = c_1 x_1 + c_2 x_2 + \cdots + c_n x_n\)
subject to
\[\begin{aligned} a_{11}x_1 + a_{12}x_2 + \cdots + a_{1n}x_n = & \ b_1 \\ a_{21}x_1 + a_{22}x_2 + \cdots + a_{2n}x_n = & \ b_2 \\ \vdots & \\ a_{m1}x_1 + a_{m2}x_2 + \cdots + a_{mn}x_n = & \ b_m \\ \end{aligned}\] \[x_1 \ge 0, x_2 \ge 0, \ldots, x_n \ge 0\]最小化一个目标函数
等式约束
变量非负
Matrix form
cost vector
\[\mathbf{c} = [ \begin{matrix} c_1 & c_2 & \cdots & c_n \end{matrix} ]^T\]solution vector
\[\mathbf{x} = [ \begin{matrix} x_1 & x_2 & \cdots & x_n \end{matrix} ]^T\]right-hand-side vector
\[\mathbf{b} = [ \begin{matrix} b_1 & b_2 & \cdots & b_n \end{matrix} ]^T\]constraint matrix
\[\mathbf{A} = \begin{bmatrix} a_{11} & a_{12} & \cdots & a_{1n} \\ a_{21} & a_{22} & \cdots & a_{2n} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ a_{m1} & a_{m2} & \cdots & a_{mn} \\ \end{bmatrix}\] \[\color{green} {\boxed{ \begin{aligned} \text{min} \quad & \mathbf{c}^T \mathbf{x} \\ \text{s.t.} \quad & \mathbf{Ax} = \mathbf{b} \\ & \mathbf{x} \ge 0 . \end{aligned} }}\]例-运输问题
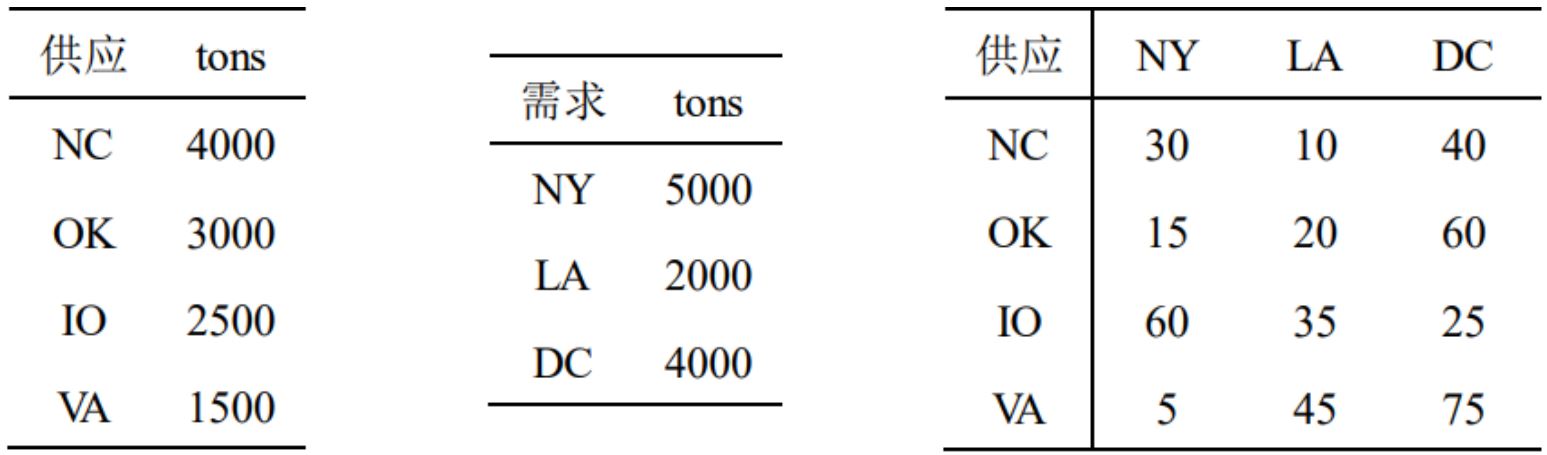
一个管理问题:如何用最经济的方法满足顾客的要求?
LP模型:
— 要引入的决策变量有哪些?
— 目标函数是什么?
— 约束条件是什么?
1.2 Embedded assumptions in LP
1.Proportionality Assumption
— no discount
— 没有回收利用的经济效益
2.Additivity Assumption
— 总影响 = 各个变量的影响之和
3.Divisibility Assumption
— 所有的小数/分数都是允许的
3.Certainty Assumption
— 每个参数都是确定的
1.3 Converting to standard form
例
\[\begin{aligned} \text{maximize} \quad & 3x_1 - 2x_2 - 4 |x_3| \\ \text{s.t.} \quad & -x_1 + 2x_2 \le -5 \\ & 3x_2 - x_3 \ge 6 \\ & 2x_1 + x_3 = 12 \\ & x_1 ,\ x_2 \ge 0 \\ \end{aligned}\]Rule 1: Unrestricted (free) variables
\[x_i^+ = \begin{cases} x_i , \quad & \text{if } x_i \ge 0 \\ 0 , \quad & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} \quad x_i^- = \begin{cases} 0 , \quad & \text{if } x_i \ge 0 \\ x_i , \quad & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\] \[x_i \in \mathcal{R} \quad \Leftrightarrow \quad \color{green}{ x_i = x_i^+ - x_i^- \quad x_i^+ ,\ x_i^- \ge 0 }\]— By product: \(\lvert x_i \rvert = x_i^+ + x_i^-\)
— Potential problem: 要求\(x_i^+ \times x_i^- = 0\)
\[\begin{aligned} \text{maximize} \quad & 3x_1 - 2x_2 - 4 (x_3^+ + x_3^-) \\ \text{s.t.} \quad & -x_1 + 2x_2 \le -5 \\ & 3x_2 - (x_3^+ - x_3^-) \ge 6 \\ & 2x_1 + (x_3^+ - x_3^-) = 12 \\ & x_1 ,\ x_2 ,\ x_3^+ ,\ x_3^- \ge 0 \\ \end{aligned}\]Rule 2: Inequality constraints
引入松弛变量和剩余变量
\[\begin{aligned} \text{maximize} \quad & 3x_1 - 2x_2 - 4 (x_3^+ + x_3^-) \\ \text{s.t.} \quad & -x_1 + 2x_2 + x_4 = -5 \\ & 3x_2 - (x_3^+ - x_3^-) - x_5 = 6\\ & 2x_1 + (x_3^+ - x_3^-) = 12 \\ & x_1 ,\ x_2 ,\ x_3^+ ,\ x_3^- ,\ x_4 ,\ x_5 \ge 0 \\ \end{aligned}\]Rule 3: Minimization of the objective function
\[\color{green}{ \text{max } \mathbf{c}^T \mathbf{x} = - \text{min } ( - \mathbf{c}^T \mathbf{x} ) }\] \[\begin{aligned} \text{minimize} \quad & - 3x_1 + 2x_2 + 4x_3^+ + 4x_3^- \\ \text{s.t.} \quad & - x_1 + 2x_2 + x_4 = -5 \\ & 3x_2 - (x_3^+ - x_3^-) - x_5 = 6\\ & 2x_1 + (x_3^+ - x_3^-) = 12 \\ & x_1 ,\ x_2 ,\ x_3^+ ,\ x_3^- ,\ x_4 ,\ x_5 \ge 0 \\ \end{aligned}\]More on free variable and absolute value
潜在问题:
1.丢失了二次型约束
2.维数增加
3.原本的一个解对应现在的多个解
4.\(|x|\)为凸函数,而\(-|x|\)为凹函数
5.当\(\mathbf{c}\)为正时,最大化\(\mathbf{c|x|}\)可能会成为问题
Reference: ‘Linear' Programming with Absolute-Vaue Functionals. David F. Shanno, Roman L. Weil. Operations Research. Vol. 19. No. 1. (Jan - Feb. 1971). pp. 120-124.
