Graph Neural Networks
Introduction
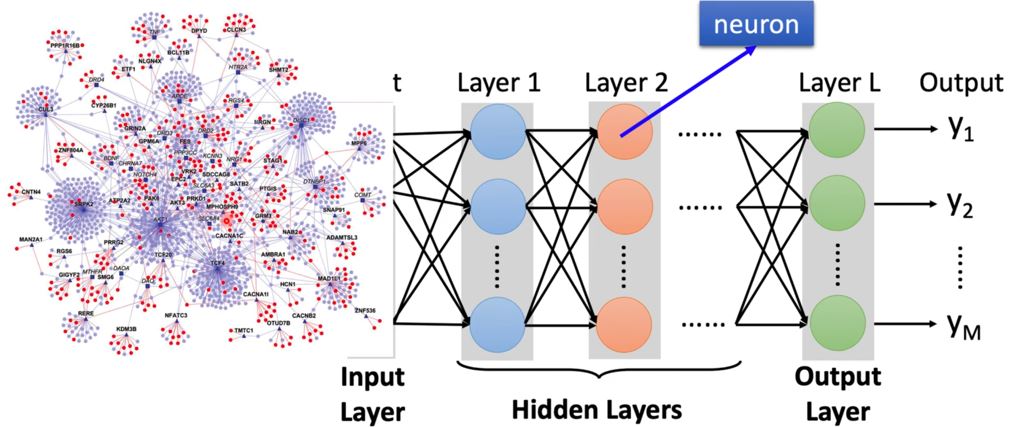
我们要怎么把一个graph塞进neural network中呢?之前我们的输入可能是一张照片、一个序列,如果我们把上面这样的图喂给model,要如何让model知道图的结构,也就是node和edge的特征呢?
为什么我们需要用GNN呢?
— GNN可以用在Classification、Generation等问题中。
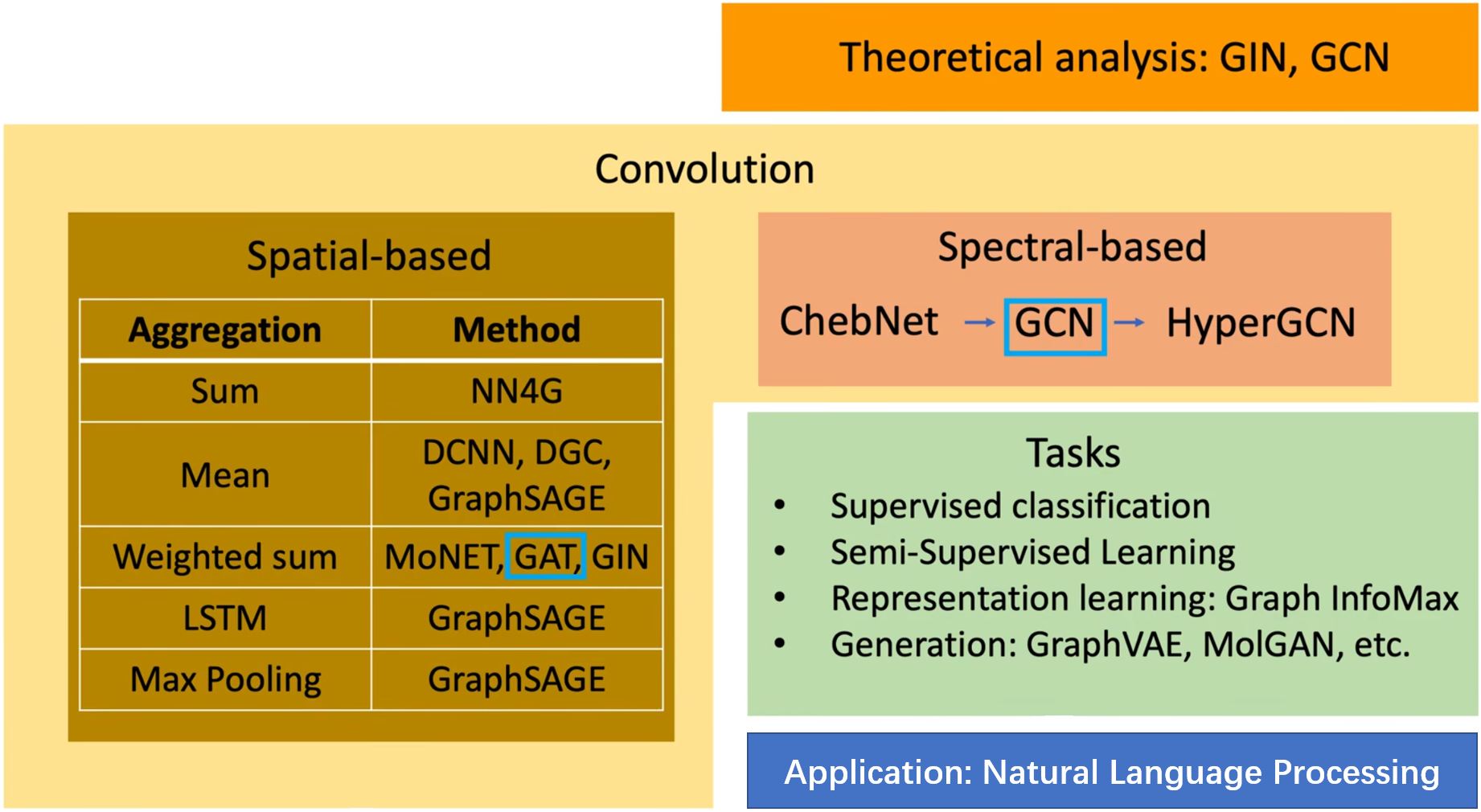
如何利用卷积将节点嵌入到一个特征空间中?
— Solution 1:将convolution (corelation)的概念推广到图中 → Spatial-based convolution
— Solution 2:回到信号处理中对convolution的定义 → Spectral-based convolution
Roadmap
Tasks, Dataset and Benchmark
Tasks:
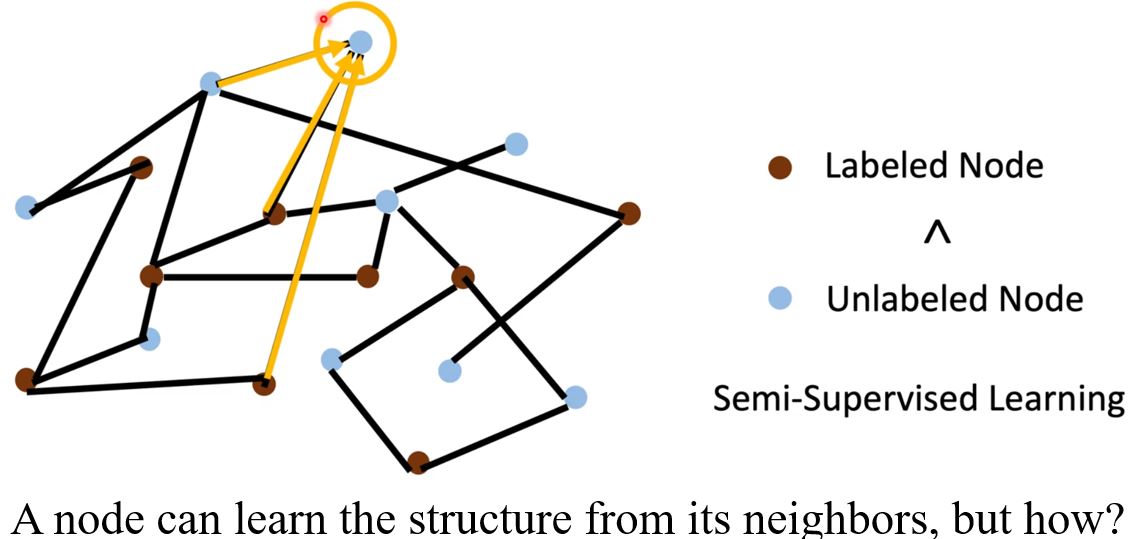
- Semi-supervised node classification
- Regression
- Graph classification
- Graph representation learning
- Link prediction
Common dataset:
- CORA: citation network. 2.7k nodes and 5.4k links
- TU-MUTAG: 188 molecules with 18 nodes on average
Spatial-based GNN
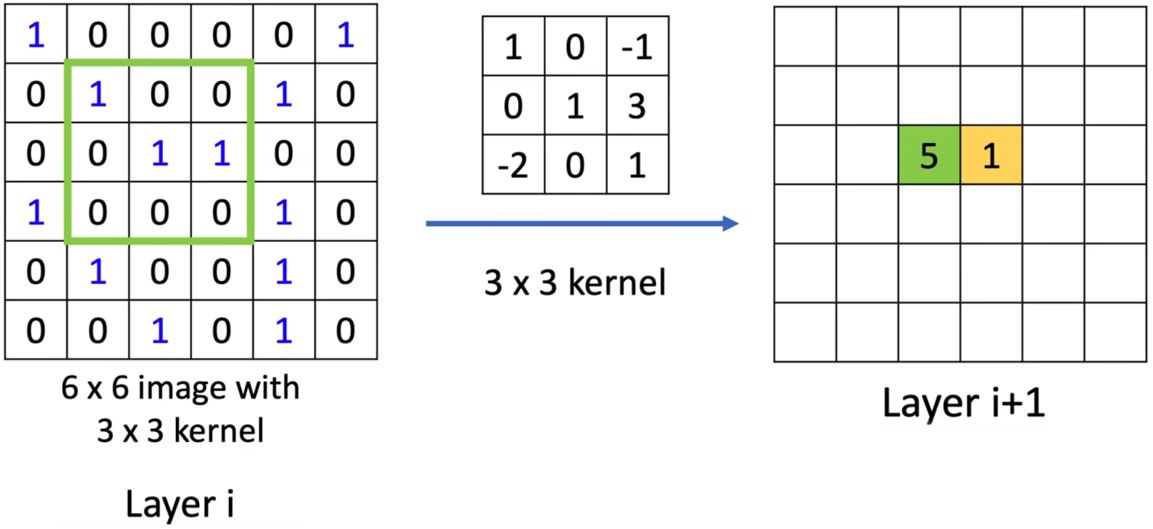
Review: Convolution
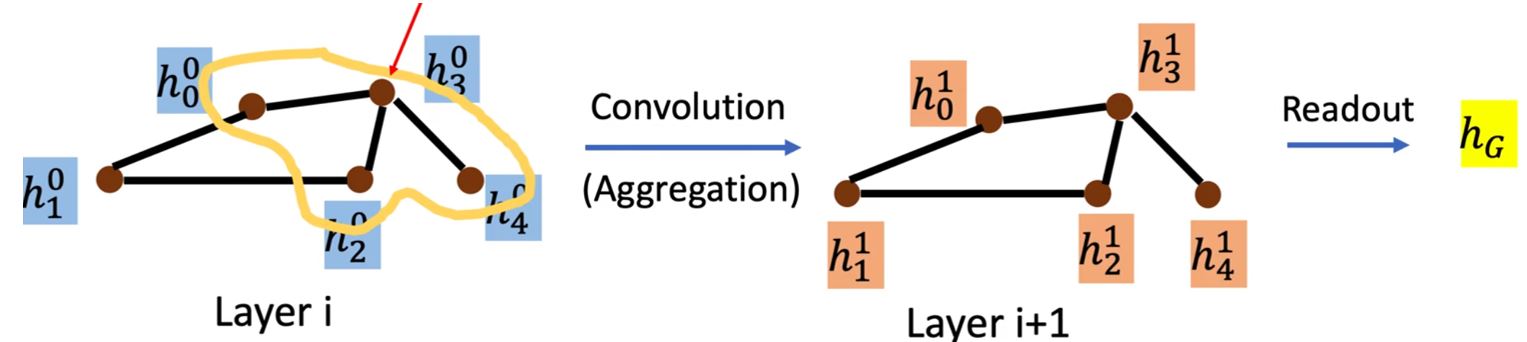
Spatial-based Convolution
Aggregate:用neighbor feature更新下一层的hidden state
Readout:把所有nodes的feature集合起来代表整个graph
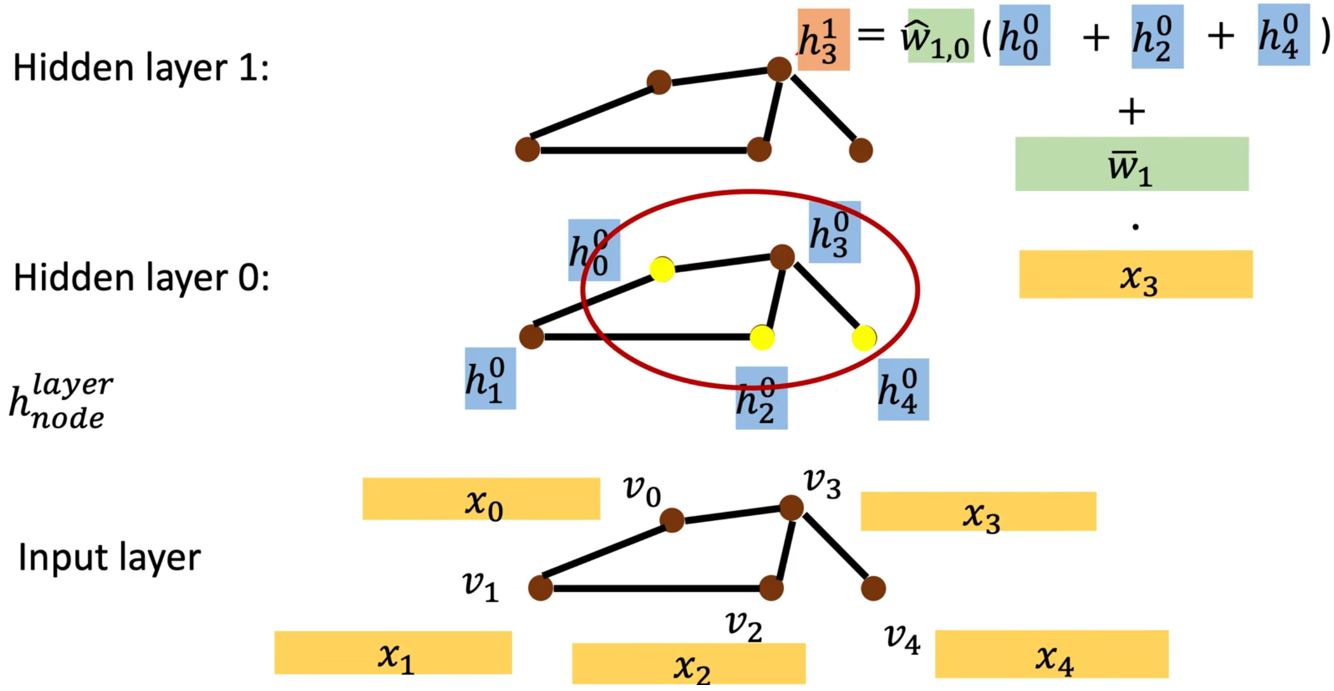
NN4G (Neural Networks for Graph)
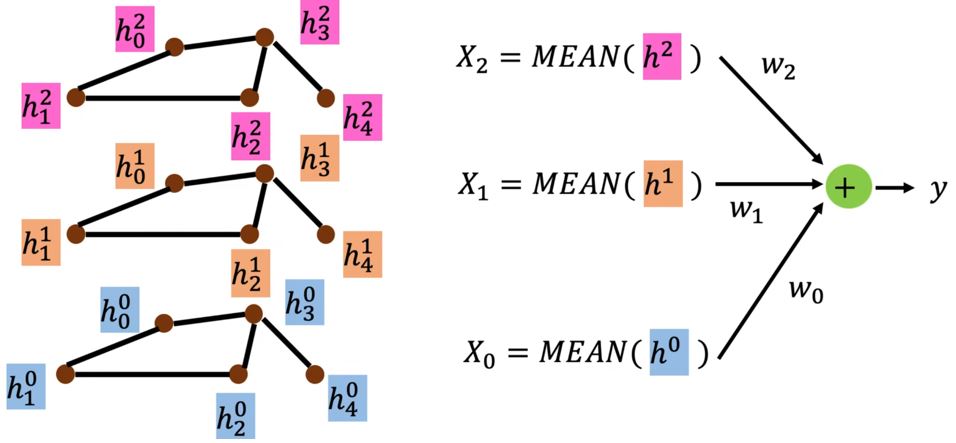
DCNN (Diffusion-Convolution Neural Network)
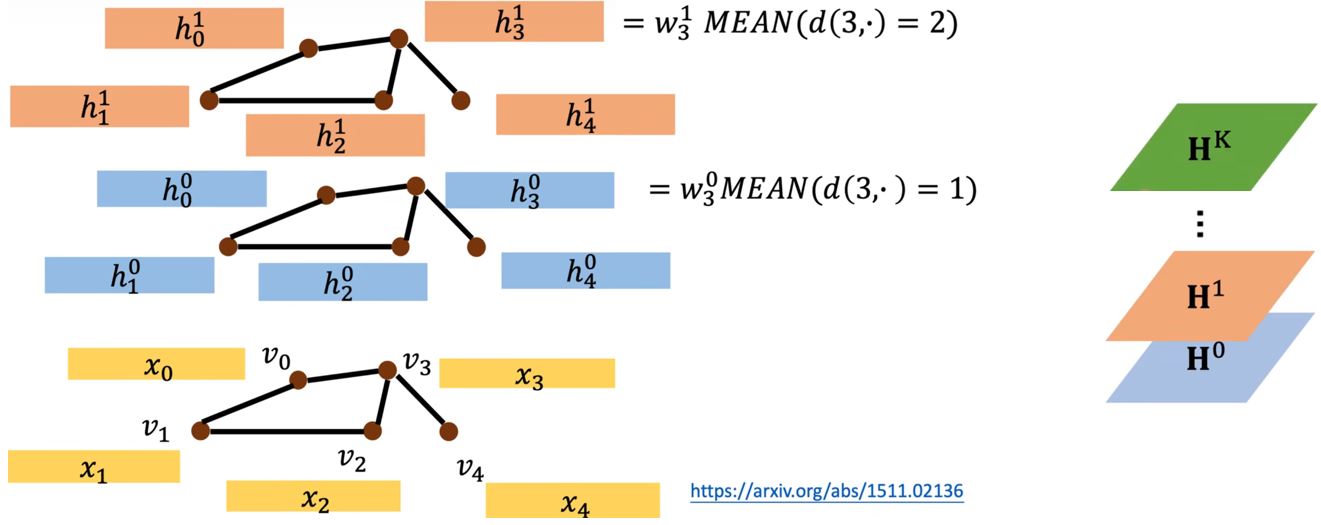
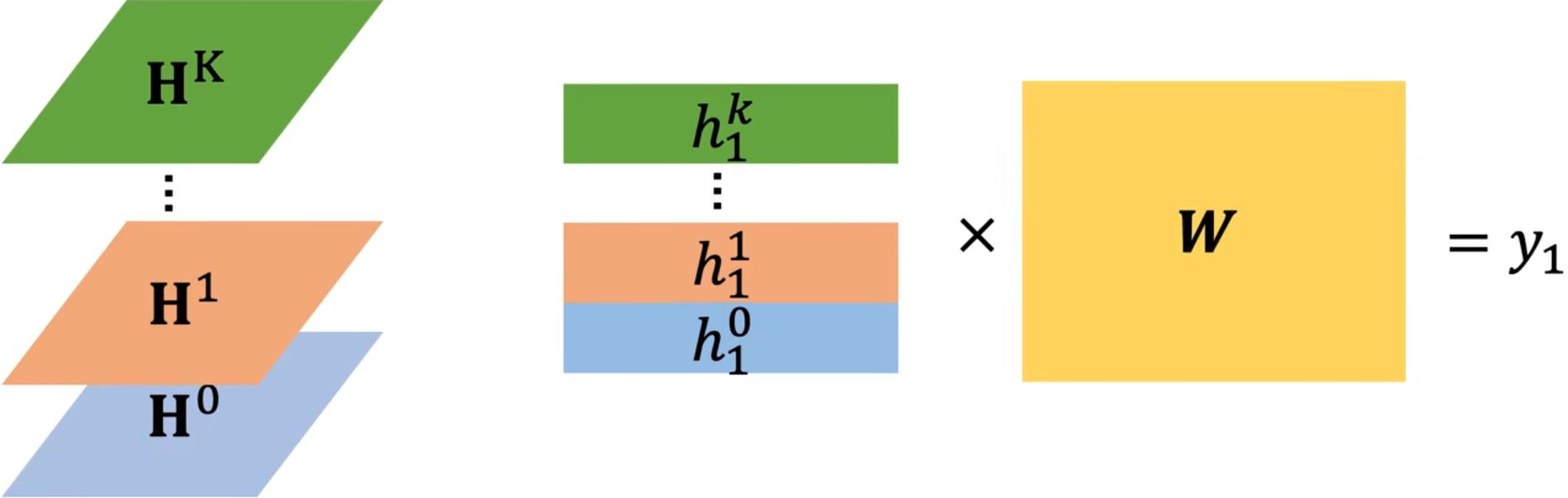
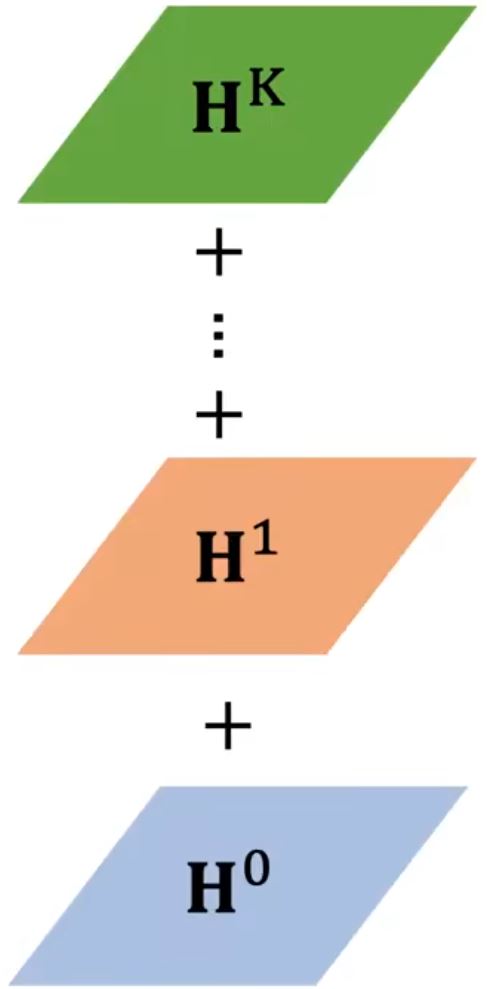
DGC (Diffusion Graph Convolution)
MoNET (Mixture Model Networks)
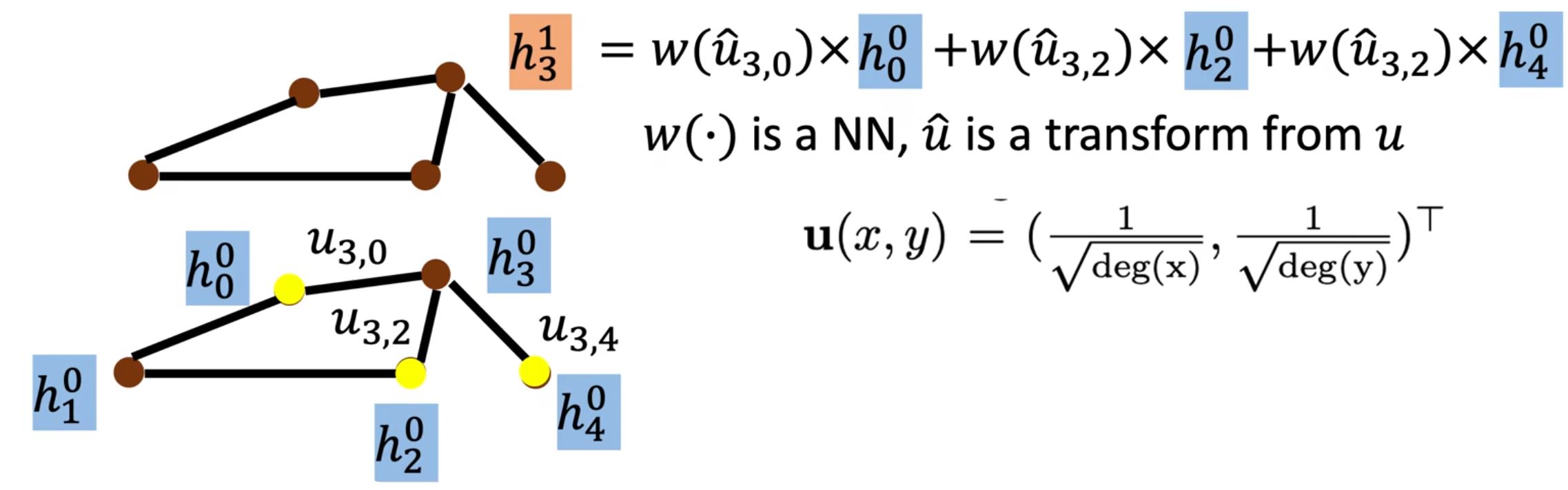
- 定义节点间"距离"的度量方
- 用加权和(平均值)而不是简单地直接把邻居节点相加(求平均)
GraphSAGE
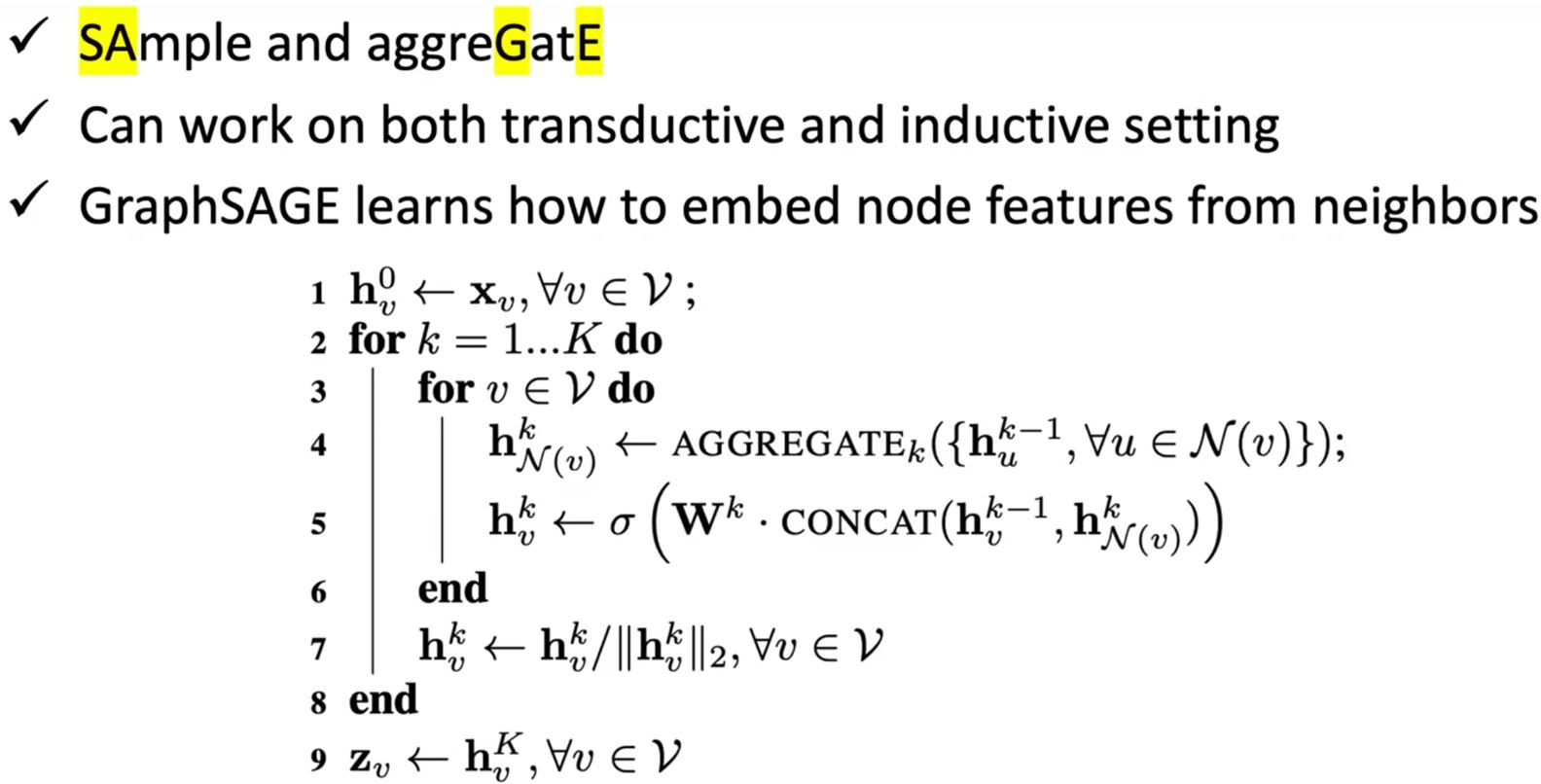
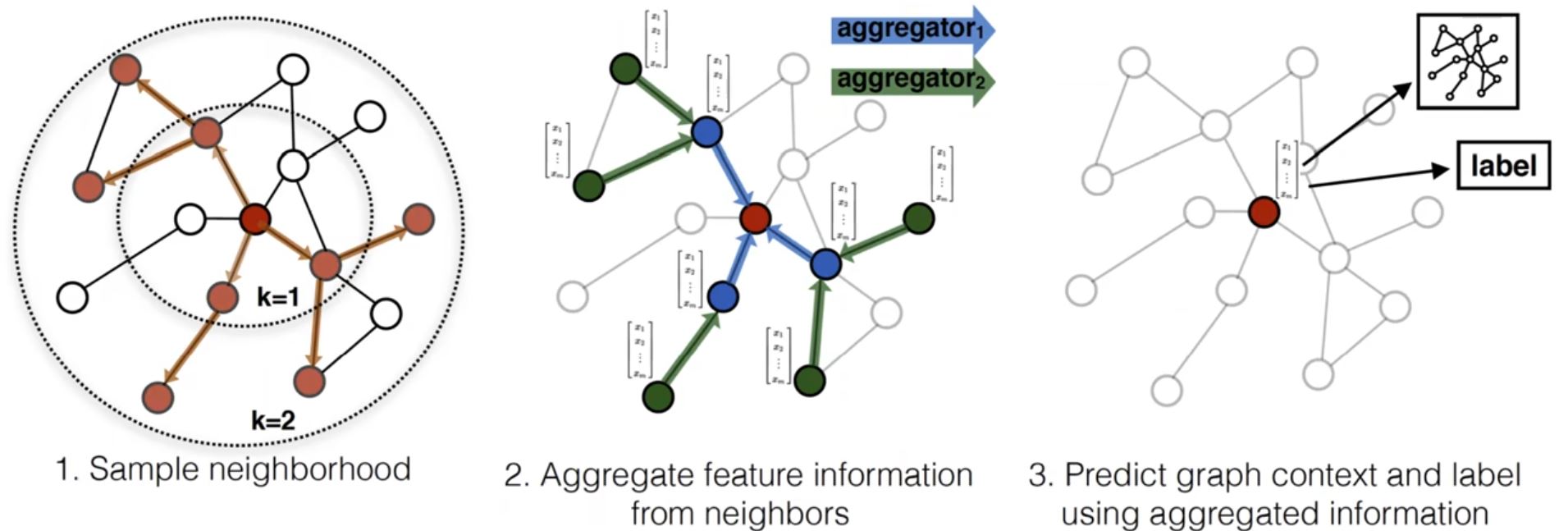
- Aggregation: mean, max-pooling or LSTM
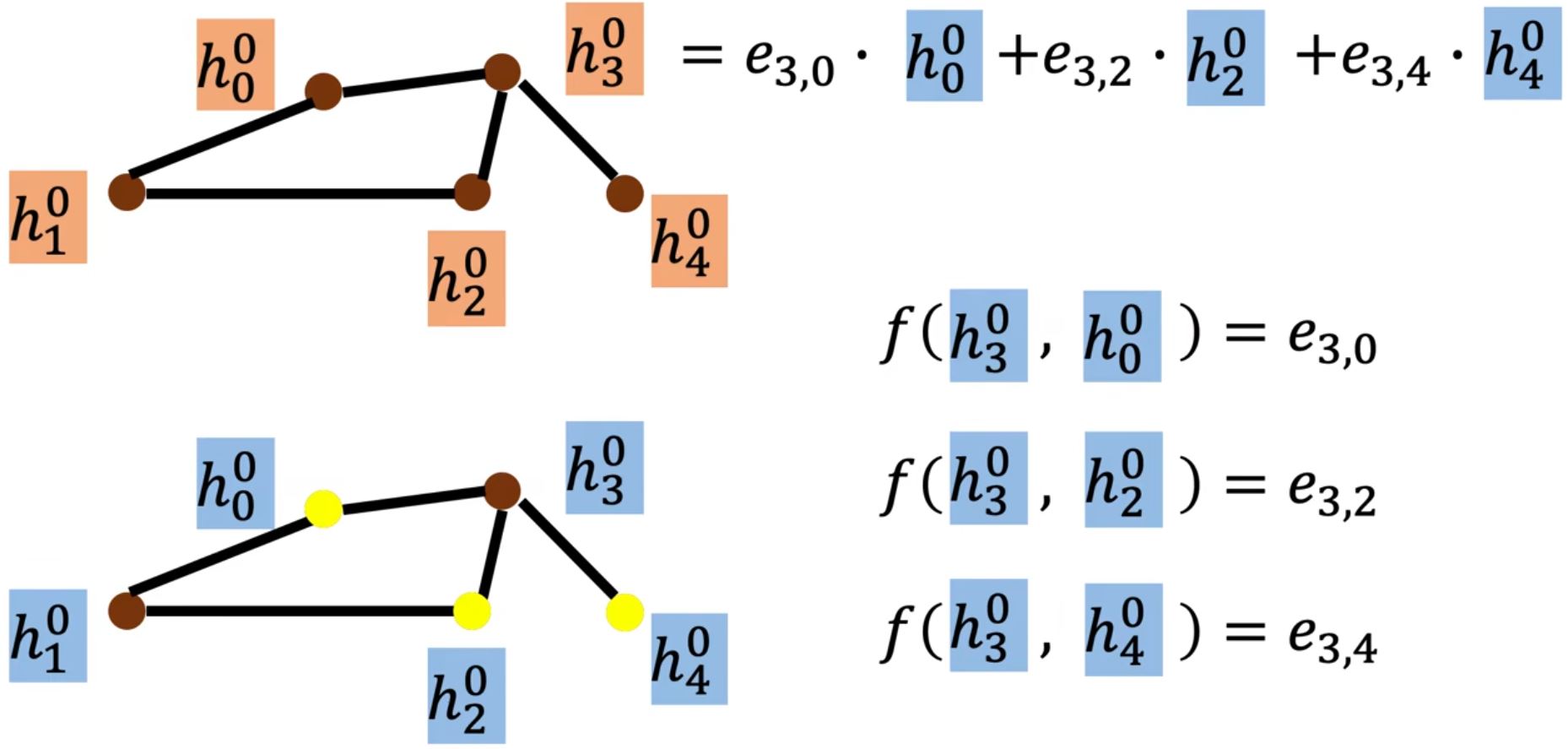
GAT (Graph Attention Networks)
GIN (Graph Isomorphism Network)
……
